Masters of story don’t start with a simple fact or assertion, they weave a story that does the same thing.
Rabbi Jonathan Sacks could have begun his speech by simply saying something like “all faiths have similarities, but they also have interesting differences.”
That would have been a perfectly coherent way to start a speech at an interfaith dinner. But by starting with a story that demonstrates the same thing, he does so much more than assert a first beat.
He demonstrates mastery of the story form, establishes his own character as a player at Government level, and also brings some laughs to the room. But the story is always in the service of demonstrating the first beat of the rest of his speech.
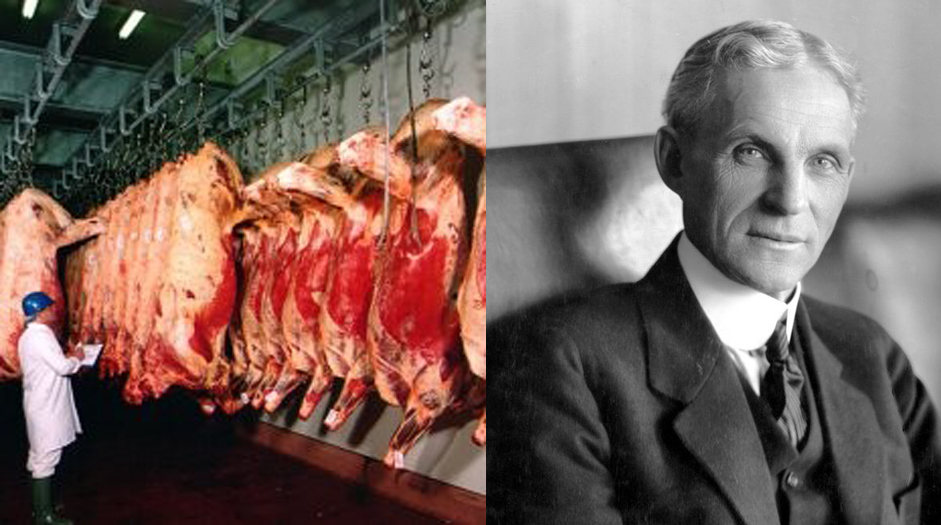
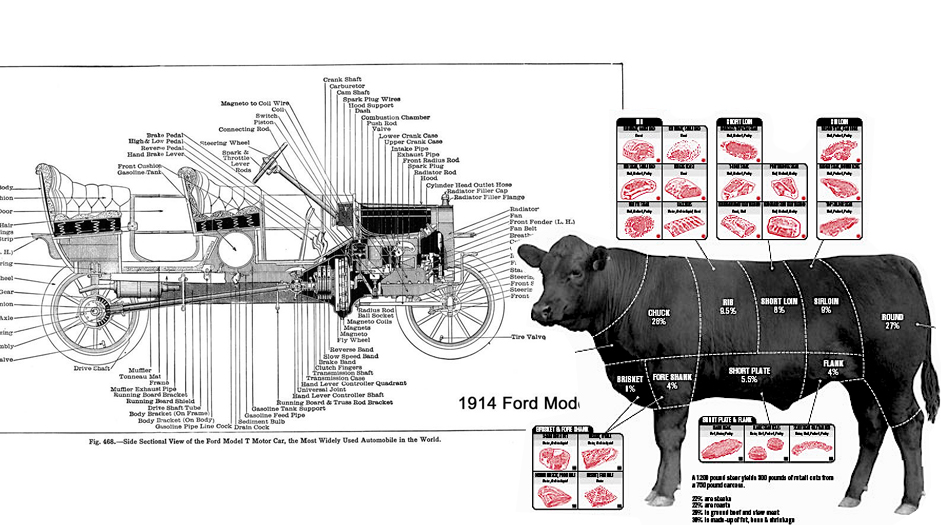 Henry Ford famously used the paradigm of meat packing to find a better way of building a car. Essentially it inverted the notion that mechanics walked around a single car, gradually constructing it over a period of months. Under Ford’s system, it was the converse; cars proceeded like cow carcasses from one specialised process to the next. Where cows were disassembled, cars were being assembled. By seeing a car as a relatively low value object he could transform its production, and produce the world’s first high volume automobile.
Henry Ford famously used the paradigm of meat packing to find a better way of building a car. Essentially it inverted the notion that mechanics walked around a single car, gradually constructing it over a period of months. Under Ford’s system, it was the converse; cars proceeded like cow carcasses from one specialised process to the next. Where cows were disassembled, cars were being assembled. By seeing a car as a relatively low value object he could transform its production, and produce the world’s first high volume automobile.